Baton Rouge, Charleston, Provo see Largest Growth in Median Wage For Mid-Sized Metros Since 2005; Youngstown Wage Declined the Most
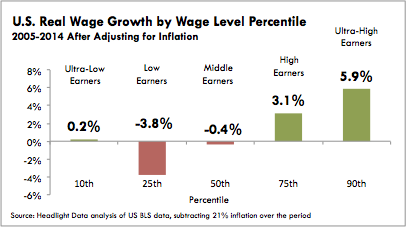
As described in a previous article for large metros, wage performance can be examined at the median wage level and also across the distribution of wages. Since 2005, Ultra-High Wage Earners in the U.S. enjoyed the fastest growing real wages (+5.9% at the 90th percentile) and Low-Wage Earners saw declining wages (-3.8% at the 25th percentile). Ultra-Low Wage Earners saw slightly positive wage growth (+0.2% at the 10th percentile). Wages are adjusted for inflation (made “real”).
(See footnote for a full explanation of percentile levels and wage groups)
Examining this wage distribution across the 51 mid-sized metros (population 500,000 up to 1 million), the fastest-growing real median wage since 2005 was in Baton Rouge (+4.2%), Charleston (+4.1%) and Provo (+3.9%). Youngstown had lowest wage growth (-9.9%), followed by Cape Coral (-6.7%) and Toledo (-6.2%).
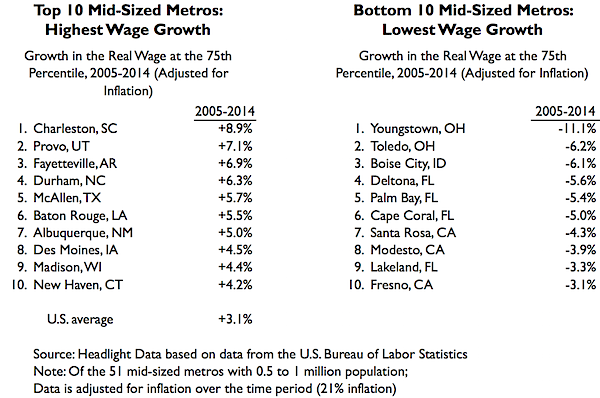
At the High Wage level (top half of all wage earners), the mid-sized metros that generated the most wage growth were Charleston (+8.9%), Provo (+7.1%) and Fayetteville (+6.9%). Youngstown had the largest High Wage decrease (-11.1%), followed by Toledo (-6.2%) and Boise City (-6.1%).
Click here to see this data mapped in Tableau Public. Permission is granted to embed this map in any website. Click the "Share" button to get the embed code.
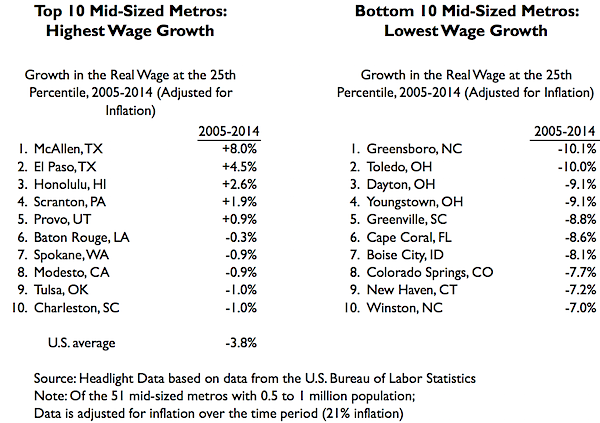
At the Low Wage Level (bottom half of all wage earners), only 5 of 51 mid-sized metros saw wages increase. McAllen led wage growth (8.0%), followed by El Paso (4.5%) and Honolulu (2.6%). Wages decreased the most in Greensboro (-10.1%), Toledo (-10.0%) and Dayton (-9.1%).
At the Ultra-High Wage level (top 20% of all wage earners), Fayetteville had the highest wage growth (16.5%), followed by Provo (14.4%) and Charleston (10.6%). Nine of 51 mid-sized metros saw wages shrink at the Ultra-High Wage level since 2005. Wages decreased most in Deltona (-6.0%), Youngstown (-4.1%) and Toledo (-3.8%).
Click here to see this data mapped in Tableau Public. Permission is granted to embed this map in any website. Click the "Share" button to get the embed code.
Note:
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics releases percentile wage estimates as part of the Occupational Employment Statistics data. The median wage is the wage of workers in the middle of the distribution of all workers. Wages are also provided at the 10th, 25th, 75th, and 90th percentile. For example, the 25th percentile wage estimate is the wage value in which 25% of workers have lower wages. In 2014, North Dakota’s 25th percentile annual wage was $25,910, meaning that 25% of North Dakota employees earned less than $25,910 that year.
The percentile wage levels are used to form the following wage groups:
- Ultra-Low Wage Earners = Bottom 20% of wage earners, whose median wage is at the 10th percentile.
- Low Wage Earners = The bottom half of all wage earners, whose median wage is at 25th percentile.
- High Wage Earners = The top half of all wage earners, whose median wage is at the 75th percentile.
- Ultra-High Wage Earners = Top 20% of all wage earners, whose median wage is at the 90th percentile.
Click here to download a spreadsheet of the data.
Research, analysis and content developed by Headlight Data.
About Headlight Data:
Headlight Data is an award-winning online data aggregator, designed for economic and workforce development organizations, that provides online, decision-support tools on the economy, demographics, education, workforce and public policy.